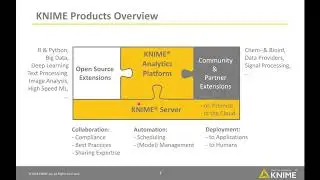
Antimalarial and Anti Wolbachia drug discovery using cheminformatics and machine learning
Neil Berry (University of Liverpool) presented a BMGF Global Health Compound Design Webinar 25/6/20. He covered two case histories showing how a combination of cheminformatics and machine learning approaches were applied to drug discovery in:
1. Antimalarial Drug Discovery: Exploring the MEP Pathway
A chemoinformatics-led high throughput screen identified the 1,2-benzoisothiazolone (BITZ) chemotype as a promising Plasmodium IspD inhibitor (IC50 = 484nM). A program of organic synthesis, guided by molecular modelling, developed SAR and suggested a mechanism of enzyme inhibition for the lead candidate molecule.
2. Anti-Wolbachia (A-WOL) Drug Discovery: Ligand Based Virtual Screening combined with HTS
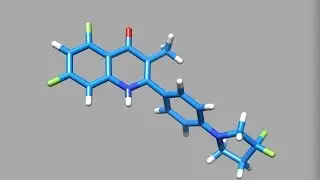
New drugs that eliminate the worm-symbiont Wolbachia bacterium can eradicate lymphatic filariasis (elephantiasis) and onchocerciasis (river blindness). Machine learning approaches were used to select successive generations of compounds for screening, combining results from HTS and ligand based virtual screening. This approach gave i) an increased hit rate, ii) expansion of SAR around hits, iii) discovery of novel hit chemotypes, and iv) probed new areas of chemical space. Neil will highlight AWZ1066S which is now in preclinical development and expected to enter clinical trial in ~12 months.