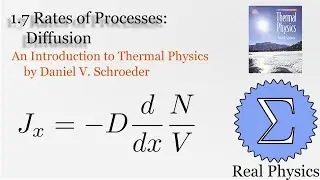
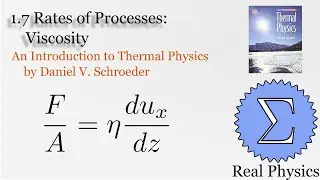
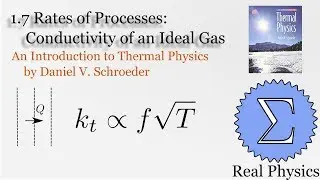
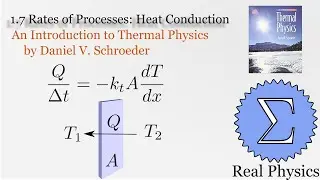
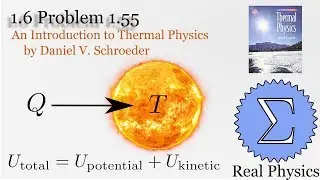
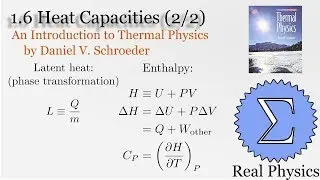
1.5 Compression Work (2 of 2) (Thermal Physics) (Schroeder)
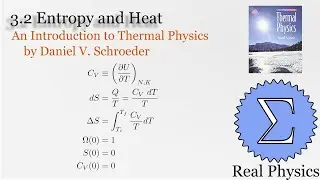
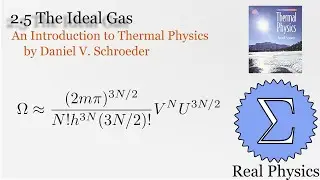
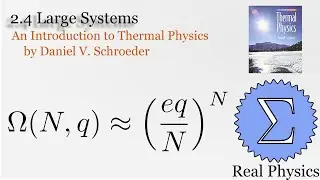
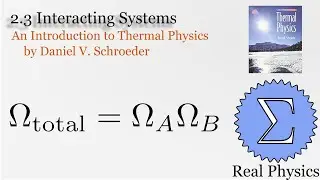
Assuming an ideal gas, we can calculate what would happen under two types of compression: isothermal (temperature and therefore internal energy remain constant) and adiabatic (no heat). Most compressions in real life will be between one or the other extremes. We derive two simple equations relating heat and work based on the change of volume of the gas.
Playlist: • An Introduction to Thermal Physics by...
Join us on Discord: / discord
You can support this channel by buying the book through this link: https://amzn.to/2Z8xEpX
You can also support the channel by donating to / realphysics . Any amount will greatly help and is very much appreciated.
The textbook I am using is: Schroeder, Daniel V. "An Introduction to Thermal Physics" 1st ed., Addison Wesley Longman, 2005.





![[MECHA TAILED SPIRIT HACK!] Roblox Shindo Life Script/Hack GUI | INFINITE SPINS, AUTO FARM & MORE!](https://images.videosashka.com/watch/no9tGV_Wul0)