Enable Cellular option in Windows
Here's how to Enable Cellular option in Windows.
i. There are a few possible reasons why cellular is not working in Windows, and some steps you can try to fix it.
One of the possible reasons is that your *SIM card* is not inserted properly, not activated, or not compatible with your device. To check this, you can try the following:
Make sure your SIM card is inserted correctly into the SIM card slot on your device. You may need a SIM card tool or a paperclip to open the slot. If you have an eSIM, make sure it's installed and activated. For more info, see Use an eSIM to get a cellular data connection on your Windows PC.
Make sure your SIM card is not locked by a PIN code. To do this, go to Settings - Network & internet - Cellular - Advanced options - SIM PIN and turn off the toggle if it's on.
Make sure your SIM card is compatible with your device and your mobile operator. You can contact your mobile operator or check their website for more info.
Another possible reason is that your *cellular settings* are not configured correctly or need to be updated. To check this, you can try the following:
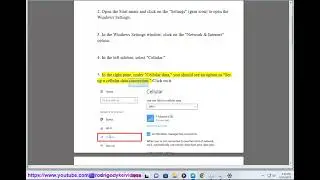
Make sure cellular is turned on and you have a cellular data plan from your mobile operator. To do this, go to Settings - Network & internet - Cellular and turn on the toggle under Cellular. If you don't see Cellular as an option, make sure you have a SIM card or an eSIM installed and activated.
Make sure you have selected the right SIM card or eSIM profile for cellular data if you have more than one. To do this, go to Settings - Network & internet - Cellular and select Use this SIM for cellular data under Advanced options.
Make sure you have entered the correct user name, password, and access point name (APN) for your cellular network. To do this, go to Settings - Network & internet - Cellular and select Advanced options - Add an APN. You can find this information from your mobile operator or on their website.
Make sure you have the latest updates for Windows and your cellular drivers. To do this, go to Settings - Update & security - Windows Update and select Check for updates. If there are any updates available, install them and restart your device.
A third possible reason is that there is a *problem with your device* or your **cellular network**. To check this, you can try the following:
Restart your device and see if that helps. Sometimes, a simple reboot can fix many issues with connectivity.
Eject and reinsert your SIM card or switch to another SIM card or eSIM profile if you have one. This can help refresh your connection and resolve any glitches.
Check if there is a good cellular signal in your area and if there are any service outages or maintenance work by your mobile operator. You can contact your mobile operator or check their website for more info.
Try connecting to another cellular network if available. You may need to change your network mode or roaming settings depending on your location and mobile operator. To do this, go to Settings - Network & internet - Cellular and select Advanced options - Network selection or Roaming options.
If none of them work, you may need to *contact your mobile operator* or *Microsoft support* for further assistance.
ii. Enabling the Cellular option in Windows is a feature that allows you to connect to the internet using a cellular data network, such as 4G or 5G. This can be useful when you are traveling or in an area where Wi-Fi or Ethernet is not available or reliable. However, there are also some pros and cons of using this feature that you should consider before enabling it. Here are some of them:
Pros:
You can access the internet from anywhere that has a cellular signal, without relying on other devices or networks.
You can enjoy faster and more stable internet speeds, especially if you have a 5G-enabled device and network.
You can use your device as a mobile hotspot and share your cellular data with other devices.
You can avoid potential security risks or privacy issues that may arise from using public Wi-Fi or unsecured networks.
Cons:
You need to have a SIM card or an eSIM profile installed on your device, and a data plan from a mobile operator to use the Cellular option.
You may incur additional costs or fees for using cellular data, depending on your data plan and usage. You may also have to pay for roaming charges if you travel to a different country or region.
You may experience lower battery life on your device, as using cellular data consumes more power than using Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
You may encounter compatibility issues or errors with some programs or features that require a specific version of Windows or a certain type of network connection.
These are some of the pros and cons of enabling the Cellular option in Windows. I hope this helps you to decide whether to use this feature or not.