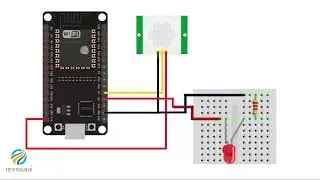
What is a thermistor? | It's working | Tutorial by Technowave G
A thermistor is a resistance thermometer, or a resistor whose resistance is dependent on temperature.
It is made of metallic oxides, pressed into a bead, disk, or cylindrical shape and then encapsulated
with an impermeable material such as epoxy or glass.
Types of thermistors:
1)Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC)
NTC is inversely proportional to resistance. This type of thermistor is used the most.
2)Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC).
PTC is directly proportional to resistance. This type of thermistor is generally used as a fuse.
Typically, a thermistor achieves high precision within a limited temperature range of about 50ºC around the target temperature.
This range is dependent on the base resistance.
In NTC the amount by which the resistance decreases as the temperature increases is not constant, it varies in a non linear way.
that why we used Steinhart-Hart equation to calculate the actual resistance of a thermistor with greater precision.
1/T = A + B(lnR) + C(lnR)3
Where:
T -is temperature, in Kelvins (K, Kelvin = Celsius + 273.15)
R -is resistance at T, in Ohms (Ω)
A, B and C are the Steinhart-Hart coefficients that vary depending on the type of thermistor and the range of temperature.
ln - is Natural Log.