Improve Search Results Using Semantic Ranking In Azure Ai | Harness The Power Of Semantic Search
Discover how to significantly improve search relevance in Azure AI Search with semantic ranking. This video provides a comprehensive guide to leveraging Azure AI Search to enhance search results using Microsoft's advanced language understanding models. Learn the steps to enable semantic ranking, configure your search index, and optimize your queries for better, more relevant search outcomes.
🔍 In this video, you'll learn:
What is semantic ranking in Azure AI Search?
How to enable and configure semantic ranking in Azure AI Search.
The benefits of semantic captions and highlights for search results.
Practical steps for setting up and querying with semantic ranking.
Understanding the pricing and availability of semantic ranking.
📈 Key Features:
Secondary ranking using BM25 or RRF in Azure AI Search.
Multi-lingual deep learning models from Microsoft Bing.
Extracting and displaying semantic captions and answers for improved search relevance.
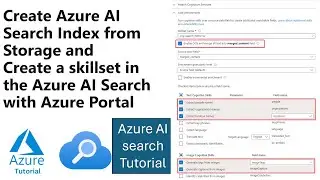
Step-by-step guide to enable semantic ranking in the Azure portal.
How to set up a semantic configuration in a search index.
Setting up queries to return semantic captions, highlights, and answers.
What is semantic ranking?
Semantic ranker is a collection of query-side capabilities that improve the quality of an initial BM25-ranked or RRF-ranked search result for text-based queries. When you enable it on your search service, semantic ranking extends the query execution pipeline in two ways:
First, it adds secondary ranking over an initial result set that was scored using BM25 or RRF. This secondary ranking uses multi-lingual, deep learning models adapted from Microsoft Bing to promote the most semantically relevant results.
Second, it extracts and returns captions and answers in the response, which you can render on a search page to improve the user's search experience.
Here are the capabilities of the semantic reranker.
Feature Description
Semantic ranking Uses the context or semantic meaning of a query to compute a new relevance score over preranked results.
Semantic captions and highlights Extracts verbatim sentences and phrases from a document that best summarize the content, with highlights over key passages for easy scanning. Captions that summarize a result are useful when individual content fields are too dense for the search results page. Highlighted text elevates the most relevant terms and phrases so that users can quickly determine why a match was considered relevant.
Semantic answers An optional and extra substructure returned from a semantic query. It provides a direct answer to a query that looks like a question. It requires that a document has text with the characteristics of an answer.
How semantic ranker works
Semantic ranking feeds a query and results to language understanding models hosted by Microsoft and scans for better matches.
Semantic ranking is both resource and time intensive. In order to complete processing within the expected latency of a query operation, inputs to the semantic ranker are consolidated and reduced so that the reranking step can be completed as quickly as possible.
There are two steps to semantic ranking: summarization and scoring. Outputs consist of rescored results, captions, and answers.
How inputs are collected and summarized
In semantic ranking, the query subsystem passes search results as an input to summarization and ranking models. Because the ranking models have input size constraints and are processing intensive, search results must be sized and structured (summarized) for efficient handling.
Semantic ranking starts with a BM25-ranked result from a text query or an RRF-ranked result from a hybrid query. Only text fields are used in the reranking exercise, and only the top 50 results progress to semantic ranking, even if results include more than 50. Typically, fields used in semantic ranking are informational and descriptive.