Coolant Temperature Sensor function. What does a coolant temperature sensor do
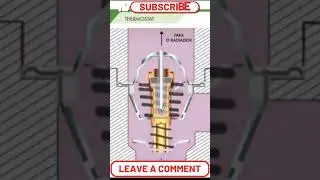
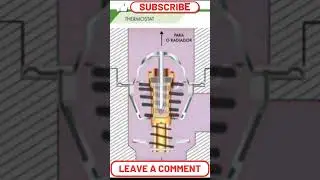
The Coolant Temperature Sensor - CTS is a crucial component of a vehicle's engine management system. Its primary function is to monitor the temperature of the engine coolant and provide this information to the Engine Control Unit - ECU.
The CTS is typically located in the engine's coolant passage, allowing it to directly measure the temperature of the coolant as it circulates through the engine.
The temperature of the engine coolant affects the air-fuel mixture required for efficient combustion. A colder engine requires a richer fuel mixture for starting and warm-up, while a warmer engine requires a leaner mixture for optimal performance and fuel efficiency. The Engine Control Unit uses the information from the Coolant Temperature Sensor to adjust the fuel mixture accordingly.
The CTS also plays a role in controlling emissions. By monitoring the coolant temperature, the ECU can activate the engine's emissions control systems, such as the catalytic converter and oxygen sensors, at the appropriate times to reduce harmful emissions.
The Coolant Temperature Sensor helps protect the engine from damage due to overheating. If the coolant temperature exceeds a certain threshold, the Engine Control Unit may trigger a warning light on the dashboard or activate engine protection measures.
In summary, the Coolant Temperature Sensor is essential for ensuring optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, emissions control, and engine protection. By providing real-time temperature data to the Engine Control Unit, it helps the engine management system make accurate adjustments to maintain efficient and reliable operation under various driving conditions.
If the temperature sensor is faulty, problems arise in the engine.