The World’s Largest Iceberg Is Headed for a Disastrous Collision with a Penguins Colony
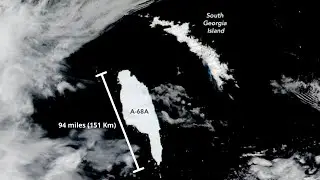
The largest block of ice that broke off from Antarctic could strike land this month. More than twice the size of Luxembourg, Iceberg A68 cracked off from Antarctica in 2017. Since then, A68a has been drifting over 1000 km northward into warmer waters. Recently, satellite images have spotted the berg drifting directly toward South Georgia
Today, the giant berg lies around 120 km from South Georgia. If it remains on its current path, the iceberg could soon reach the island’s shores. With a surface area similar to A68a’s, the island ecosystem could be seriously disrupted if the berg makes landfall. The island serves as the breeding ground for hundreds of thousands of seals and penguins. The iceberg could easily block their routes preventing them from feeding their young. It could also disturb the ecosystem by crushing animal and plant life on the seafloor. There's still a chance that ocean currents could carry A68a around the island's coast rather than directly into it. If that happens, the vast quantities of dust riding aboard A68a could fertilize nearby ocean plankton. Sending those nutrients up the food chain to fish, penguins and seals