319 - What is Simulated Annealing Optimization?
319 - What is Simulated Annealing Optimization?
Code link: https://github.com/bnsreenu/python_fo...
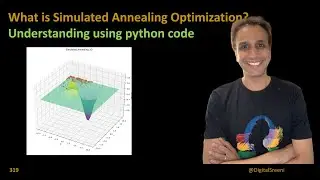
Simulated annealing is inspired by the physical process of annealing, in which a material is gradually cooled to form a crystalline structure with a minimum energy state.
It works by iteratively adjusting the temperature of the system and accepting or rejecting candidate solutions based on a probabilistic function that depends on the current temperature and the change in the objective function value.
At high temperatures, the algorithm accepts solutions with a worse fitness to explore the search space and avoid local optima. As the temperature decreases, the algorithm becomes more selective and converges to a better solution.
The cooling schedule determines the rate of temperature reduction and plays an important role in the algorithm's performance.
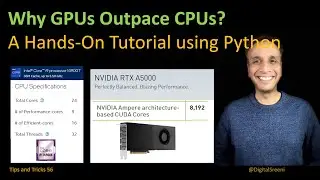
Simulated annealing is well-suited for finding the global optimum in a large search space with many local optima, such as in combinatorial optimization and network design problems.
Simulated annealing has been used for image registration, object tracking, and texture synthesis in microscopy images.