ArchiCAD Tutorial | Multi-Story Buildings: Basic & Advanced Strategies
http://www.acbestpractices.com - In this excerpt from the Best Practices Course ArchiCAD training website, several methods of modeling multiple story buildings are demonstrated, starting simply then gradually getting to a more sophisticated process that will generate very clean section drawings with lots of detail.
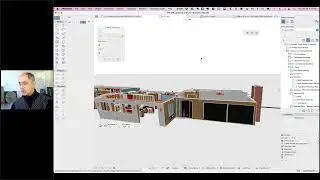
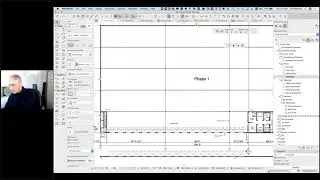
In variation 1, walls are stacked on top of each other, with slabs placed inside the face of the walls. In variation 2, the slab is placed between the lower and upper walls. In both cases, the result in 3D and in elevation is clean; in section, the model creates a simple schematic drawing that does not detail the construction components.
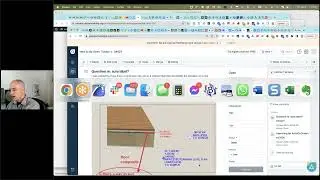
In variation 3, the walls are changed into composites to show more detail of the wall assembly. The slab is embedded into the lower wall, then subtracted out using ArchiCAD's versatile Solid Element Operations palette. The resulting section drawing is much more accurate than before.
The demonstration continues, exploring how to make different materials for the floor and walls in different rooms by cutting the slab and some of the walls into separate pieces. Some subtle Wall Priority settings are shown that control how the split walls clean up to each other, which helps make the elevations look right.
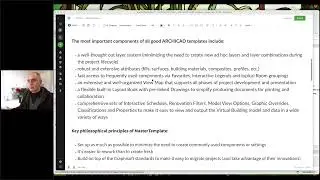
In a final variation, complex profiles are created for three different wall assemblies that include notches or extra bump-outs to match the actual construction section details. Once created, these profiles are as easy to use as standard composite walls, and result in even more detailed and accurate section drawings.
Finally, an excerpt from MasterTemplate (http://www.actemplate.com) is shown to demonstrate how much further a complex wall profile can be taken. In this case, internal wall framing as well as waterproofing details are included in the wall and are instanlty seen in great detail in the section drawing.