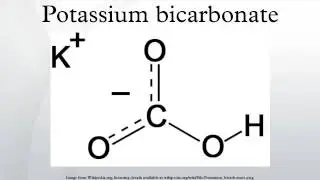
Monospaced font
A monospaced font, also called a fixed-pitch, fixed-width or non-proportional font, is a font whose letters and characters each occupy the same amount of horizontal space. This contrasts with variable-width fonts, where the letters differ in size from one another, as do spacings in between many letters. The two high use letters 'I' and 'E' in both cases simply do not need the same footprint, while both differ in center to next letter edge (and center to center) spacing distance needs (margins) in variable width fonts. The variable that changes is the offset from what would otherwise be monspaced centering. In a modern proportional font every dimension can be scaled and change, but such sizing mathematically must still maintain monospacing or variable spacing.
Note that this article generally assumes Western (Latin-based, Cyrillic, or Greek) writing systems. East Asian rules of typography, for example, require CJK fonts to be always monospaced at least as far as the main characters for writing words (i.e. not punctuation) are concerned. Other scripts vary in their use of monospaced fonts.
This video is targeted to blind users.
Attribution:
Article text available under CC-BY-SA
Creative Commons image source in video